Text input
Text inputs enable the user to interact with and input content and data. This component can be used for long and short form entries.
Overview
There are instances, sometimes in the same form, where you need users to enter both short and long form content. Allow the size of the text input box to reflect the length of the content you expect the user to enter.
| Variant | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Text input | When the expected user input is a single line of text, as opposed to a paragraph. |
| Text area | When the expected user input is more than one sentence. |
Live demo
<div><TextInputhelperText="Optional helper text"id="test2"invalidText="A valid value is required"labelText="Text input label"placeholder="Placeholder text"/></div>
Formatting
Default values
Where possible, add programmatic assistance. Detect and pre-fill inputs to reduce errors and save time. When the software can’t determine the value that belongs in an input, use type-ahead to make suggestions. Use sentence-case for default values, detected values, and auto-completion text.
Validation and errors
Real time validation helps to streamline the process and keep data clean when the user is filling out forms. For full guidelines, refer to the forms usage page.

Character count
Text fields and text areas may have a character limit and counter. Use the character limit and counter to let users know how long their entry can be before they begin typing.
While useful for data collection, character count is not an intuitive way to communicate content length to users. Character count allows a user to understand an input error if they surpass the character limit.

Content
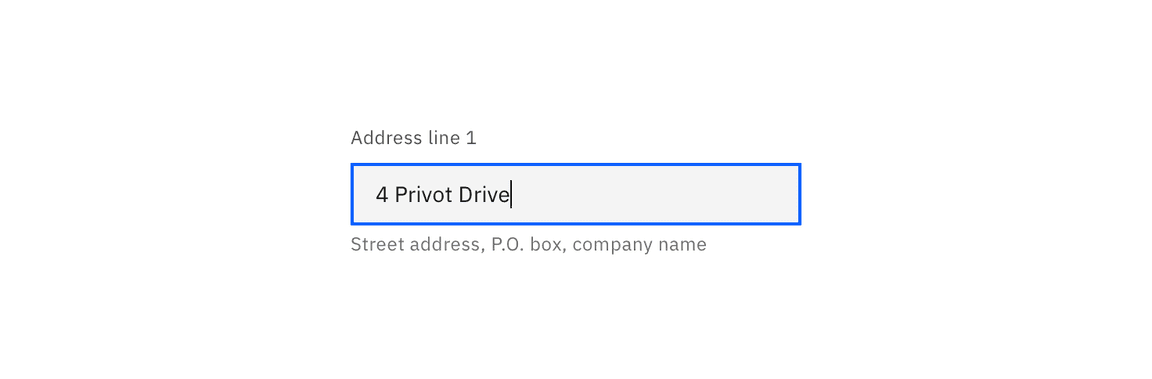
Labels
Effective form labeling helps users understand what information to enter into a text input. Using placeholder text in lieu of a label is sometimes employed as a space-saving method. However, this is not recommended because it hides context and presents accessibility issues.
Accessibility best practices for labels
- Labels must be visible when an input gets focus.
- Labels must be announced to the screen reader on focus.
- Ensure the helper text that appears under an input is read when an assistive technology user stops at an input using ARIA.
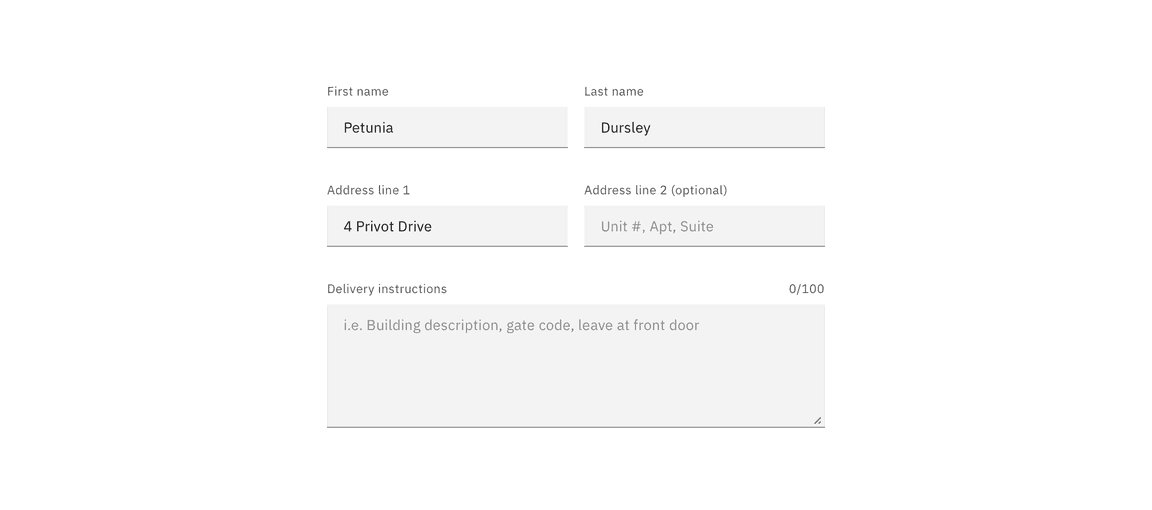
Placeholder text
Placeholder text provides hints or examples of what to enter. Placeholder text disappears after the user begins entering data into the input and should not contain crucial information. Use sentence-style capitalization, and in most cases, write the text as a direct statement without punctuation.

Helper text
Helper text is pertinent information that assists the user in completing a field. Helper text is always available when the input is focused and appears underneath the label. Use sentence-style capitalization, and in most cases, write the text as full sentences with punctuation.
Feedback
Help us improve this component by providing feedback, asking questions, and leaving any other comments on GitHub.